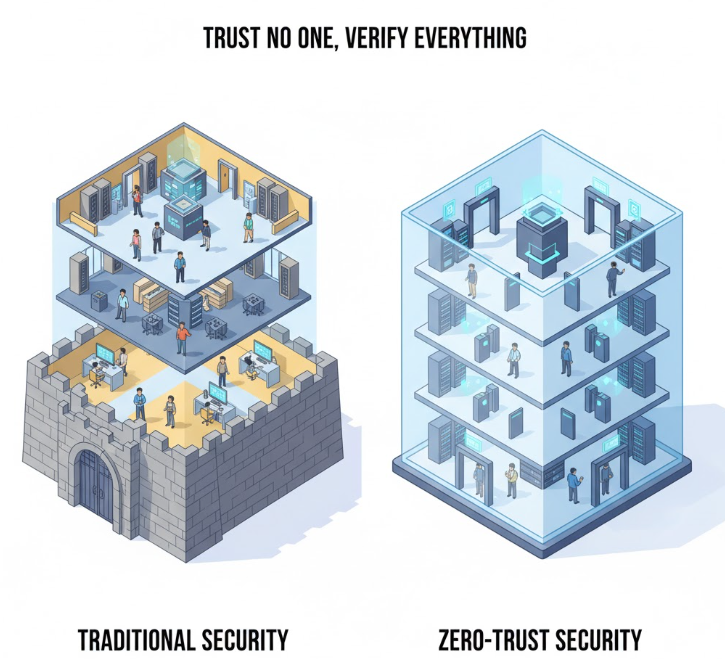
Introduction: The Modern Security Challenge
Traditional perimeter-based security models are increasingly ineffective in a world of cloud apps, remote work, and distributed networks. Organizations face rising cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and insider risks. Zero-trust networking addresses these challenges by assuming that no user or device should be inherently trusted.

What Is Zero-Trust Networking?
Zero-trust networking is a modern security model where every access request is continuously verified, regardless of location. It enforces strict identity verification, least-privilege access, and micro-segmentation to protect sensitive data and applications.
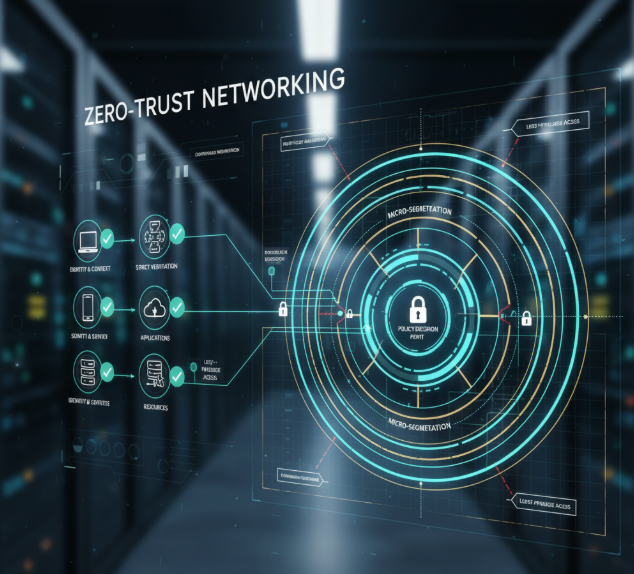

Core Principles
- Verify explicitly: Authenticate and authorize every user and device.
- Least privilege access: Grant access only to necessary resources.
- Micro-segmentation: Isolate applications and network segments.
- Continuous monitoring: Track and analyze behavior for anomalies.
Benefits of Zero-Trust Security
- Reduced attack surface: Limits lateral movement and insider threats.
- Enhanced visibility: Centralized monitoring provides insights into all access requests.
- Compliance alignment: Helps meet regulatory requirements like NIST, HIPAA, and GDPR.
- Adaptability: Works across cloud, on-prem, and hybrid environments.
Implementing Zero-Trust Networking
Organizations typically approach zero-trust adoption in phases.
Step 1: Map Your Assets and Users
Identify critical data, applications, and user roles.
Step 2: Define Access Policies
Establish least-privilege access rules and micro-segment critical systems.
Step 3: Deploy Identity and Access Controls
Use multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), and device verification.
Step 4: Monitor and Respond
Continuously analyze logs, detect anomalies, and refine policies.
OmniLegion can assist organizations in deploying zero-trust models with expert IT security consulting and network architecture guidance: https://omnilegion.com/get-it-help/
Real-World Example
Clients working with OmniLegion often combine cloud security controls, segmentation, and continuous monitoring to successfully implement zero-trust frameworks. See our IT security case studies for detailed examples: https://omnilegion.com/case-studies
FAQs
What is zero-trust networking?
A security model where no device or user is trusted by default and access is continuously verified.
How does zero-trust differ from traditional security?
Traditional security relies on perimeter defenses; zero-trust verifies every request, regardless of network location.
Can zero-trust work for cloud and remote workers?
Yes. Zero-trust is ideal for hybrid, cloud, and distributed environments.
What tools support zero-trust security?
Identity providers, MFA, SSO, micro-segmentation platforms, and SIEM tools.
Why should SMBs consider zero-trust?
It reduces risk, enhances visibility, and simplifies compliance without heavy infrastructure.
Ready to Implement Zero-Trust Security?
If your organization seeks to strengthen cybersecurity with zero-trust networking or adopt modern security models, OmniLegion provides strategic guidance and hands-on support. Contact us today: https://omnilegion.com/contact-us/.