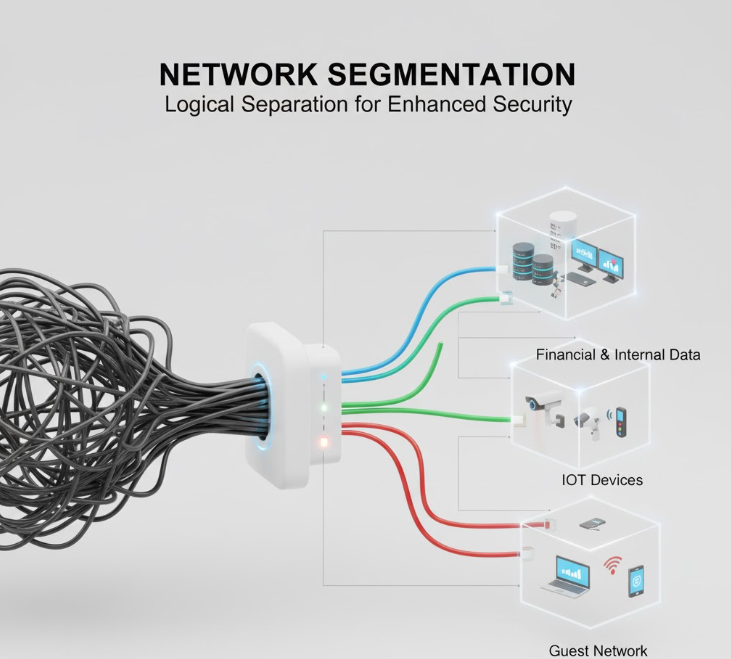
Introduction: Why Modern Networks Need Smarter Segmentation
Enterprise networks are growing more complex. Hybrid work, cloud adoption, and the rise of IoT have created sprawling environments—often without clear boundaries. When everything sits on the same flat network, performance drops and security risks multiply. This is why many IT teams rely on VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) to bring order, structure, and protection to their infrastructure.
VLAN Explained: The Simple Definition
A VLAN is a logical segmentation of a network—allowing you to group devices based on function, department, or security level, even if they’re not physically in the same location. Think of it as creating separate “virtual neighborhoods” within your switching environment.
Why VLANs Matter for Enterprise IT
- Stronger security: Isolate sensitive workloads and reduce lateral movement (aligned with NIST Zero Trust principles).
- Better performance: Reduce broadcast traffic and keep network segments efficient.
- Operational control: Enforce policies per team, workload, or compliance requirement.
- Scalability: Support growing environments without redesigning physical topology.
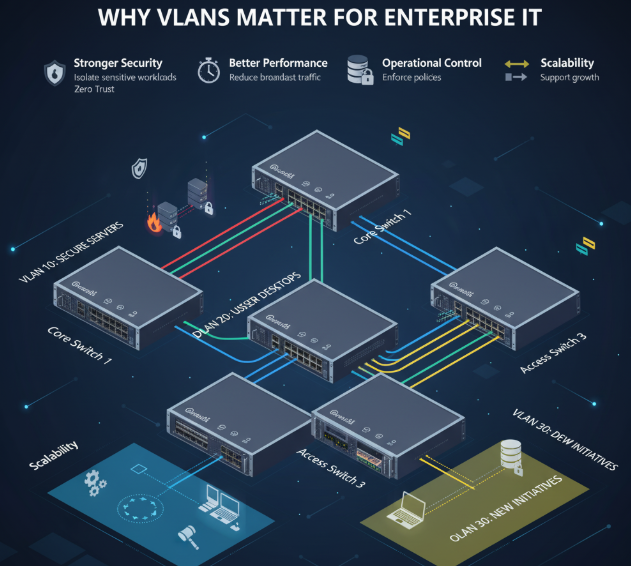
How VLANs Fit Into Switching Fundamentals
At the switching layer, VLANs function by tagging traffic (typically using IEEE 802.1Q) to keep segments separate as packets move through the network.
Access vs. Trunk Ports
- Access ports: Connect end devices; untagged traffic belonging to a single VLAN.
- Trunk ports: Carry multiple VLANs between switches or firewalls; tagged traffic.
This simple distinction enables large-scale segmentation without additional hardware.
A Practical Framework for Using VLANs
IT leaders can use this approach to design effective segmentation:
1. Map Your Functional Groups
Common segmentation examples:
- Finance and HR systems
- IoT and guest networks
- Servers, VoIP devices, and endpoints
2. Apply Least Privilege Network Access
Restrict inter-VLAN communication using ACLs or firewall policies.
3. Align with Security Standards
Follow NIST SP 800-207 Zero Trust guidelines for microsegmentation.
4. Monitor and Optimize
Use telemetry and traffic analytics (Microsoft Defender for IoT, or similar tools) to refine segmentation.
Real-World Use Case
Many OmniLegion clients segment their cloud, on-prem, and hybrid environments to reduce audit scope and mitigate threats. Explore similar examples in our IT transformation case studies at https://omnilegion.com/case-studies.
FAQs
What problems do VLANs solve?
They reduce broadcast traffic, isolate sensitive assets, and improve overall network security.
Do VLANs improve cybersecurity?
Yes—by limiting lateral movement, they enhance Zero Trust segmentation and reduce breach impact.
Can VLANs span multiple switches?
Absolutely. Using trunk links, VLANs can extend across your entire Layer 2 domain.
How do VLANs relate to Zero Trust?
VLANs enable foundational segmentation—critical before implementing full microsegmentation.
Are VLANs still relevant in cloud and hybrid environments?
Yes. Even with cloud-native networking, segmentation remains essential for compliance and performance.
Ready to Strengthen Your Network Architecture?
If you’re exploring network segmentation or need help designing secure switching architectures, OmniLegion can guide you. Contact us at https://omnilegion.com/contact-us/ to get expert support.